food protein induced enterocolitis syndrome fpies adults
The only way to prevent a Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES reaction is to strictly avoid the culprit food in the diet. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobin E IgE-mediated food hypersensitivity disorder that primarily affects formula-fed infants and young children 12.

Dietary Management Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Adult cases have been recently reported but are rare.

. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare food allergy that affects the gastrointestinal GI tract. Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES sometimes referred to as a delayed food allergy is a severe condition causing vomiting and diarrhea. There are a variety of foods that have been reported to trigger FPIES.
Li Andrew Wong-Pack Andrea Leilani Macikunas Harold Kim Allergy Asthma Clinical Immunology volume 16 Article number. The preventive diet will only be implemented if at the time of the FPIES. Classic symptoms of FPIES include profound vomiting diarrhea and dehydration.
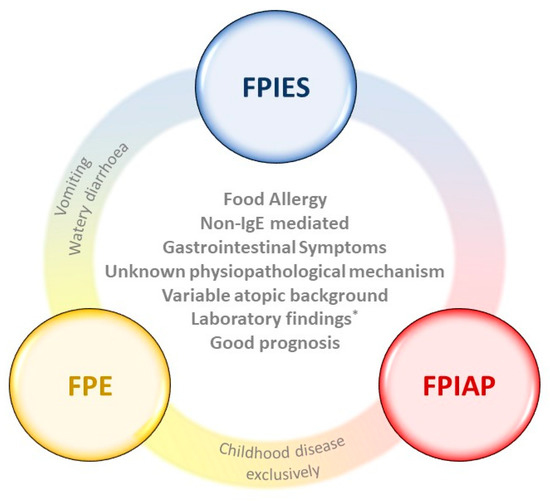
Prevention and Management. Non-IgE cell-mediated food allergic disorders encompass food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES food protein-induced allergic proctocolitis FPIAP food protein-induced enteropathy Heiners syndrome pulmonary hemosiderosis celiac disease and cows milk CM protein-induced iron deficiency anemia. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology in Practice Cambridge MA 8 5 17021709.
Most of the reactions were due to seafood mollusks crustaceans and fish and egg but other foods like peanut almond mushroom corn chicken and duck were also implicated. Insights from 441 Children with FPIES as Provided by Caregivers in the International FPIES Association. The bad thing about FPIES is that realistically any food can be a trigger.
Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES is a type of food allergy affecting the gastrointestinal GI tract. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a potentially severe presentation of non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy non-IgE-GI-FA with heterogeneous clinical manifestations. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been increasingly described in adults.
Instead it can take hours before severe symptoms begin. Its pathophysiology is still poorly understood. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE cell-mediated food allergy that manifests with repetitive projectile vomiting within 14 hours following food ingestion frequently accompanied by pallor lethargy and may be followed by diarrhea within 68 hours.
In some cases symptoms can progress to dehydration and shock brought on by low blood pressure and poor blood circulation. 12 Because celiac disease is traditionally. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a condition with heterogeneous features ie age at presentation severity food triggers comorbidities and is not as rare as initially believed.
1 In about 1520 of the reactions severe dehydration with hypotension and metabolic derangements. The clinical manifestation of FPIES is characterized by profuse and repetitive vomiting usually occurring within a few hours of feeding accompanied by lethargy and pallor. FPIES prevalence which still needs to be accurately determine in different populations appears to be higher than previously thought ie up to 07 in infants in the 1st year of life.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated gastrointestinal food allergic disorder that has gained a major interest the past decade. Food-protein induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated reaction affecting predominantly infants and children. The term enterocolitis specially refers to inflammation of the small and large intestines.
Acute FPIES reactions typically present with delayed repetitive vomiting lethargy and pallor within 1 to 4 hours of food ingestion. Unlike most food allergies symptoms of FPIES do not begin immediately after eating. FPIES mainly affects infant and young children although cases have been reported in adults.
Written in collaboration by. The FPIES Foundation Board of Directors and Medical Advisory Board. Foods that cause FPIES.
The International FPIES Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Association is a recognized 501c3 nonprofit corporation and organization that provides education support and advocacy for individuals with Food Protein-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES and. Its symptomatology is restricted to gastrointestinal manifestations and the onset of allergic reaction subsequent to exposure is delayed. Also sweet potatoes peas banana egg and fish can be a trigger.
High risk foods include milk soy rice oats and poultry. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-immunoglobulin E. A majority of cases occur during infancy particularly with the early introduction of additional foods.
The same is true for the breast-feeding mother if there is a clear connection between breast milk intake and the babys symptoms. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a non-IgE-mediated food allergy. Harizaj Schultz F Nowak-Wegrzyn A.
Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is an uncommon disorder characterized by an allergic reaction to food that affects the gastrointestinal system. This is different from the common triggers in kids which are dairy soy oats rice and banana among others. In the last few years the first population-based epidemiologic study few prospective birth cohort evaluating FPIES prevalence and several larger 100 patients.
A Slice of Food ProteinInduced Enterocolitis Syndrome FPIES. Moderate risk foods that trigger FPIES include squash carrot white potato green beans apple. Many allergists report that symptoms suggestive of FPIES are on occasion reported by adult patients and mainly refer to ingestion of seafood.
Chronic FPIES typically presents with. In this study we report a Canadian cohort of 19 adolescents and adults with recurrent non-immunoglobulin E IgE-mediated gastrointestinal symptoms after crustacean ingestion consistent with FPIES. Acute FPIES is typically characterized by profuse vomiting and lethargy occurring classically 14 hours after ingestion of the offending food.
Adults with possible food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome with crustacean ingestion Daniel H. The most common trigger is shellfish followed by fish egg peanuts almonds chicken and dairy. Food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome FPIES is a rare non-immunoglobulin E-mediated gastrointestinal food allergy primarily diagnosed in infancy but has also been reported in older children and adults.
Adults with possible food protein-induced enterocolitis syndrome with crustacean ingestion Abstract. Food protein-induced enterocolitis FPIES an entity previously thought to only affect children has been.
Foods Free Full Text Non Ige Mediated Gastrointestinal Food Protein Induced Allergic Disorders Clinical Perspectives And Analytical Approaches Html

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Food Challenge Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Management Of Acute Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Emergencies At Home And In A Medical Facility Sciencedirect

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies

Clinical Manifestations Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Scientific Diagram

Oral Food Challenge In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Download Table

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram
Two Case Reports Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis

Interpretation Of The Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Oral Download Table

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Not So Rare After All Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology

Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Proctocolitis

Clinical Types Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome Fpies Download Scientific Diagram

Managing Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome During The Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic Annals Of Allergy Asthma Immunology

References In Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome The Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology In Practice

Classification Scheme Of Fpies Fpies Food Protein Induced Download Scientific Diagram

Gastrointestinal Immunopathology Of Food Protein Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome And Other Non Immunoglobulin E Mediated Food Allergic Diseases Sciencedirect